FTP - File Transfer Protocol
This section will cover ways to enumerate File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
Table of Contents
- Overview
- FTP Configuration
- FTP Commands
- Connecting to a Server
- vsFTPd status
- vsFTPd Detailed Output
- Downloading all Files
- Enumerating FTP
- Netcat
- Telnet
- FTP with SSL/TLS Encryption
Overview
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) runs within the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol stack. These protocols also work with the support of browsers or email clients to perform their services. There are also special FTP programs for File Transfer Protocol.
FTP allows us to upload or download files to and from a server. In an FTP connection, two channels are opened.
FTP Runs on two ports:
- TCP Port 20 (FTP Data)
- TCP Port 21 (FTP Control)
First, the client and server establish a control channel through TCP port 21. The client sends commands to the server, and the server returns status codes. Then both communication participants can establish the data channel via TCP port 20.
Port 20 is used exclusively for data transmission, and the protocol watches for errors during this process. If a connection is broken off during transmission, the transport can be resumed after connection has been re-established.
There are two modes for FTP - active and passive.
In FTP active mode, the client establishes the connection as described via TCP port 21 and informs the server via which client-side port the server can transmit its responses. However, if a firewall protects the client, the server cannot reply because all external connections are blocked. This can be overcome by FTP passive mode.
In FTP passive mode, the server announces a port which the client can establish the data channel. Since the client initiates the connection, the firewall does not block the transfer.
Active mode is good if the firewall is configured with "Block all incoming, allow all outgoing". Instead of the server connecting to the client, it will be the client connecting to the server.
FTP Active Mode:

FTP Passive Mode:

To connect to a FTP server, we will need credentials. These credentials are transmitted in clear-text and can be sniffed. However, there is also a possibility that a server offers anonymous FTP where no password is required. This comes with security risks and are often best practice to not be used.
FTP Configuration
One of the most used FTP servers on Linux is vsFTPd. The default configuration of vsFTPd can be found in /etc/vsftd.conf.
On debian, to install vsFTPd, we can use the following command:
apt install vsftpd
To view the default configuration, we can use the command cat /etc/vsftpd.conf.
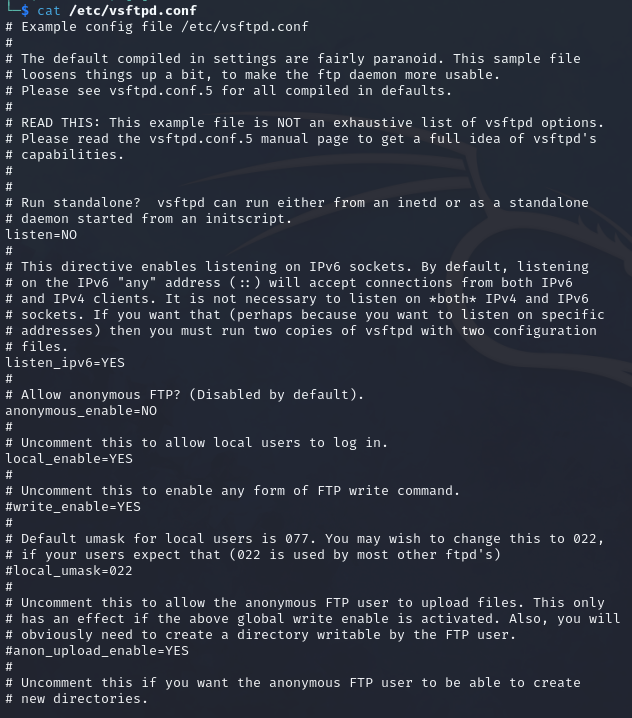
There are other FTP servers with more functionality and configuration options. This section will use vsFTPd server as it is simple to understand and very widely used.
To view the options in the configuration file, we can use the command:
cat /etc/vsftpd.conf | grep -v "#"
Command breakdown:
cat /etc/vsftpd.conf- Displays the file contents.|(pipe) - Send the output to the next command.grep -v "#"- Remove any lines that starts with the pound/hash symbol.
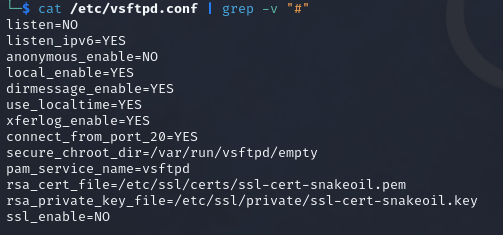
The table below lists the options and their descriptions:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| listen=NO | Run from inetd or as a standalone daemon? Yes/No. |
| listen_ipv6=YES | Listen on IPv6? Yes/No. |
| anonymous_enable=NO | Enable Anonymous access? Yes/No. |
| dirmessage_enable=YES | Display active directory messages when users go into certain directories? Yes/No. |
| use_localtime=YES | Use local time? Yes/No. |
| xferlog_enable=YES | Activate logging of uploads/downloads? Yes/No. |
| connect_from_port_20=YES | Connect from port 20? Yes/No. |
| secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty | Name of an empty directory. |
| pam_service_name=vsftpd | This string is the name of the PAM service vsftpd will use. |
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem/rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key/ssl_enable=NO | The last three options specify the location of the RSA certificate to use for SSL encrypted connections. |
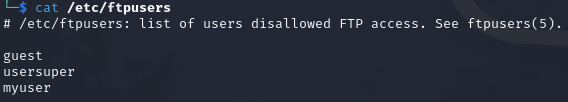
In addition to the above, there is a file called /etc/ftpusers that we need to pay attention to. This file is used to deny certain users from accessing the FTP service.
For example, the users "guest", "usersuper", and "myuser" are not permitted to log in to the FTP service.
FTP Commands
The below table will list some common FTP commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| status | Display the current status of the connection. |
| debug | Enable debugging mode. |
| ls / ls -R | List the current directory/Recursive listing. |
| get File_Name | Download a file from the server to our machine. |
| put File_Name | Upload a file to the server. |
The below are some useful commands we can use alongside or with FTP.
Connecting to a FTP Server
To connect to a FTP server, we can use the command ftp IP_ADDRESS_HERE. An example will be:
ftp 10.42.0.1
Command breakdown:
10.42.0.1- Specify the remote host to connect to.
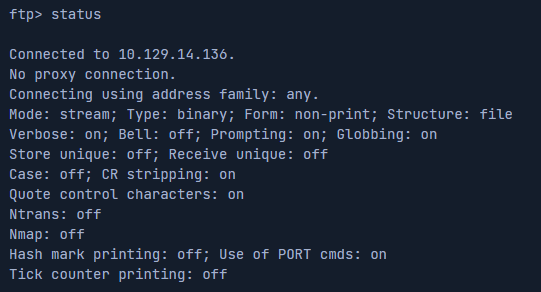
vsFTPd Status
Using the "status" command in FTP will list the connection status.
vsFTPd Detailed Output
We can use the debug and trace to get a more detailed output.
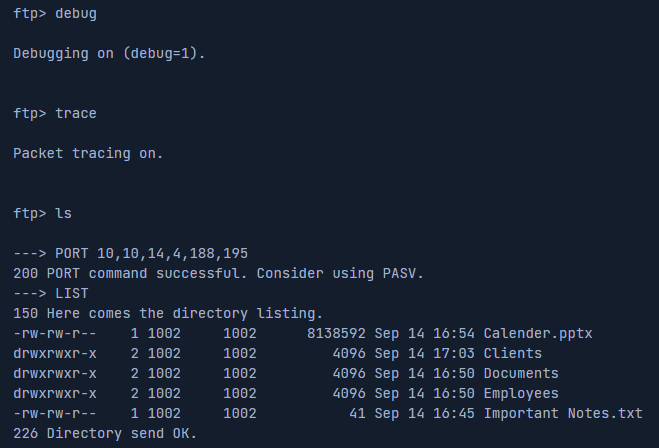
The below table will list some settings and their purpose:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| dirmessage_enable=YES | Show a message when they first enter a new directory? Yes/No. |
| chown_uploads=YES | Change the ownership of anonymously uploaded files? Yes/No. |
| chown_username=username | The user who is given ownership of anonymously uploaded files. |
| local_enable=YES | Enable local users to login? Yes/No. |
| chroot_local_user=YES | Place local users into their home directory? Yes/No. |
| chroot_list_enable=YES | Use a list of local users that will be placed in their home directory? Yes/No. |
| hide_ids=YES | All user and group information in directory listings will be displayed as "ftp". |
| ls_recurse_enable=YES | Allow the use of recurse listings. |
In the following example, we can see that if the hide_ids=YES setting is present, we will not be able to see the ownership of the directories and files, making it more harder to identify the owners of the files.
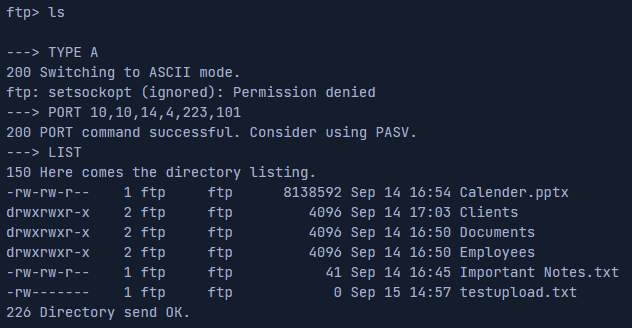
This is a security feature to prevent local usernames from being revealed thus, making it harder to perform enumeration. If the usernames are revealed, it can possibly open the system to brute force attacks as all the attacker has to do is find out the password.
Having the ability to download and upload files to and from a FTP server can potentially allow us to exploit vulnerabilities such as Local File Inclusion (LFI) where we can make the host execute system commands. Attacks are also possible with the FTP logs, which can lead to remote code execution (RCE).
Download all files
We can use wget to download all available files to our own machine from a FTP server.
wget -m --no-passive ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.2.50
Command breakdown:
-m- Specify to turn on the mirroring feature. Allows wget to download all associated files.--no-passive- Turns off passive FTP transfer mode.ftp://anonymous:anonymous@10.10.2.50- Specify the FTP serverusername:passwordand IP address of the server.
Enumerating FTP
To footprint FTP, we can use tools such as nmap and its scripting engine. To get the version of the service, we can simply perform a version scan on all ports using the following command:
nmap -sV -p- 10.42.0.2
Once we have our port number, we can use the -A flag and scripts made to enumerate FTP using the --script switch in nmap.
We can also use netcat or telnet to interact with the FTP server:
Netcat
nc -nv 10.42.0.2 21
Command breakdown:
-nv- Disable DNS resolution and use verbose mode.10.42.0.2- The target to connect to.21- The port on the target to connect to.
Telnet
telnet 10.42.0.2 21
Command breakdown:
10.42.0.2- Target to connect to.21- Port to connect to on the target.
FTP with SSL/TLS Encryption
If the target is using SSL/TLS encryption, we will also need a client that can support it. For this, we can use openssl. The good thing about openssl is that we can see the SSL certificate, which can be helpful.
openssl s_client -connect 10.42.0.2:21 -starttls ftp
Command breakdown:
-connect 10.42.0.2:21- Specify the target and the port to connect to.-starttls ftp- Upgrade the connection to a secure connection. Theftpspecifies the service to FTP.